2/1(월)
Spring DI 전략 3
전략3부터는 XML쓰지 않고 자바 코드로 컨테이너 설정 함
Configuration 어노테이션과 @Bean 어노테이션 사용한다.
전략2단계에서 @Component는 클래스 위에 선언했었다.
@Configuration도 비슷한 역할
전략1에서 전략3 사용방법
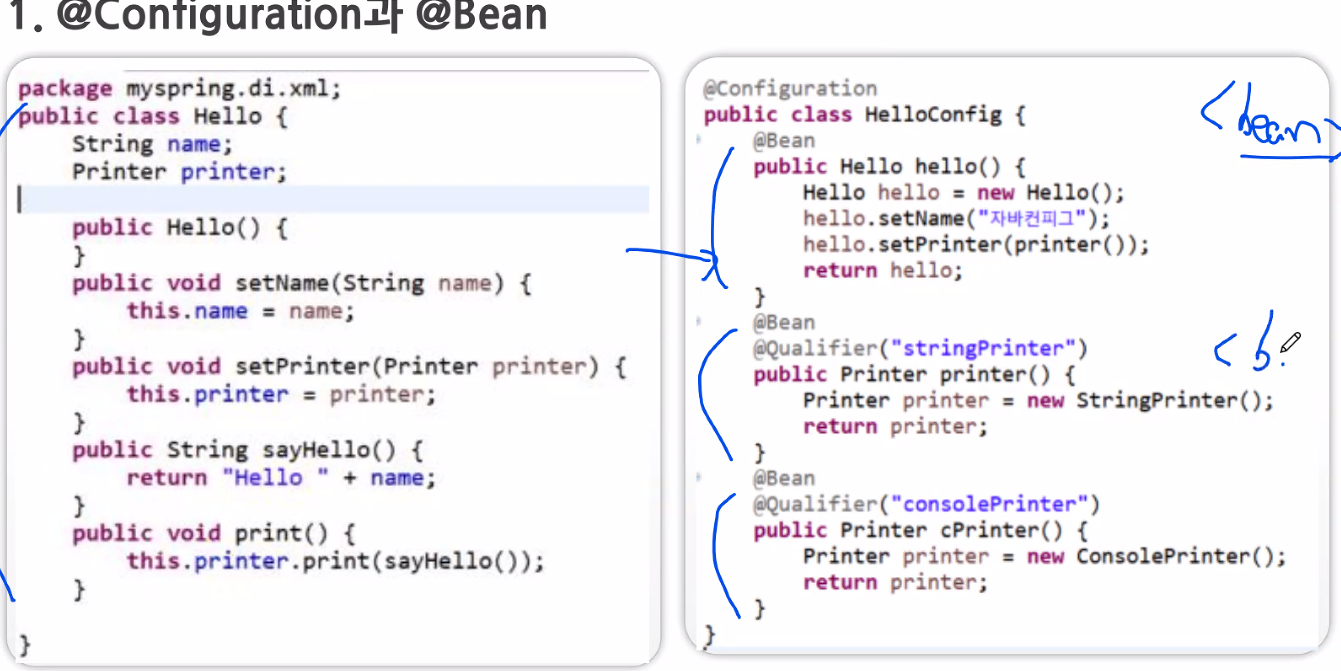
설정 역할을 하는 자바 클래스 위엔(XML역할을 하는 자바 클래스 위에는)
@Configuration 붙인다.
@Configuration
: 설정 역할을 하는 JAVA 클래스위에 선언된다.
@ComponentScan
: <context:component-scan base-package="" />
: XML에 이렇게 썻던걸 대신하는 어노테이션..
: Spring Bean(Component)를 Auto Scanning 해주는 역할, 설정 클래스 위에 선언
: 설정 클래스 위에 선언
@Bean
: <bean id="" class""/>
: Spring Bean으로 선언해주는 역할
: 메서드 위에 붙는다.
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
@PropertySource
사용법 ( 아래 클래스에 대한 설정파일과 테스트를 해볼 것이다.)
package myspring.di.annot;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("helloBean")
public class HelloBean {
// <property name="name value="어노테이션" />
// 이거랑 똑같은거다.
@Value("${name}")
private String name;
// <property name="printer" ref="stringPrinter" />
// @Autowired
// @Qualifier("stringPrinter")
@Resource(name="${printer}")
private PrinterBean printer;
public HelloBean() {
System.out.println("Hello Default constructor called");
}
// @Autowired
// public HelloBean(@Value("생성자어노테이션")String name,
// @Qualifier("stringPrinter")PrinterBean printer) {
// this.name = name;
// this.printer = printer;
// }
public HelloBean(String name, PrinterBean printer) {
this.name = name;
this.printer = printer;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("Hello setName() called" + name);
this.name = name;
}
public void setPrinter(PrinterBean printer) {
System.out.println("Hello setPrinter() called" + printer.getClass().getName());
this.printer = printer;
}
public String sayHello() {
return "Hello" + this.name;
}
public void print() {
this.printer.print(sayHello());
}
}
configuration package생성 후 configuration class생성
이후 아래와 같이 만들어준다.
package myspring.di.annot.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
@Configuration
//<!-- DI전략2의 Component Auto Scanning 설정 -->
//<context:component-scan base-package="myspring.di.annot" />
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"myspring.di.annot"})
//<!-- Properties 파일 만들것이다. -->
//<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:config/values.properties"/>
@PropertySource("classpath:config/values.properties")
public class HelloBeanConfig {
}
전략3에서 Testcase 만들 때, XML이 없기 때문에
@ContextConfiguration()에서 Config Class를 알려줘야한다.
그 후 설정XML을 사용할 때 생성됬던 Spring 컨테이너 역할을 하는 클래스(GenericXmlApplicationContext)를 사용했었다. 그러나 전략3에서는
설정 클래스 사용할 때 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 컨테이너 클래스를 사용해야 한다.
package myspring.di.annot.config.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.springframework.test.context.support.AnnotationConfigContextLoader;
import myspring.di.annot.HelloBean;
import myspring.di.annot.config.HelloBeanConfig;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = HelloBeanConfig.class, loader = AnnotationConfigContextLoader.class )
public class HelloBeanConfigTest {
@Autowired
HelloBean hello;
@Test
public void config1() {
System.out.println(hello.sayHello());
}
}
@Bean사용법
@Bean은 @Component와 같은 역할을 한다.
아래 클래스에 대한 Config파일과 테스트를 진행할것이다.
package myspring.di.xml;
import java.util.Map;
public class Hello {
private String name;
private Printer printer;
private Map<Integer,String> myMaps;
public Hello() {
System.out.println("Hello Default constructor called");
}
public Hello(String name, Printer printer) {
this.name = name;
this.printer = printer;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("Hello setName() called" + name);
this.name = name;
}
public void setPrinter(Printer printer) {
System.out.println("Hello setPrinter() called" + printer.getClass().getName());
this.printer = printer;
}
public Map<Integer,String> getMyMaps() {
return myMaps;
}
public void setMyMaps(Map<Integer, String> myMaps) {
this.myMaps = myMaps;
}
public String sayHello() {
return "Hello" + this.name;
}
public void print() {
this.printer.print(sayHello());
}
}
또한 아래 XML파일 설정값에 대한 것이다.
<!-- Hello Bean 설정 -->
<!--
scope종류
1. singleton (default) : 객체 생성 하나만하겠다.
2. prototype : 객체 생성 항상 한다.
3. request, session : 웹에서 사용하는 스코프, session이 request 보다 범위가 넓음.
-->
<bean id="hello" class="myspring.di.xml.Hello" scope="singleton">
<!-- Setter Injection 설정 -->
<property name="name" value="스프링이다." />
<property name="printer" ref="strPrinter" />
<property name="myMaps">
<map>
<entry key="100" value="스프링클라우드" />
<entry key="200" value="스프링배치" />
<entry key="300" value="스프링쿠버네티스" />
</map>
</property>
</bean>
package 생성하고, config 파일생성한다.
Property 파일에 있는 값들을 주입한다.
그러니까 여기 보면... Printer stringPrinter(){} 메서드,
Printer consolePrinter() 메서드위에 @Bean이 붙은 것을 볼 수 있다.
package myspring.di.xml.config;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import myspring.di.xml.ConsolePrinter;
import myspring.di.xml.Hello;
import myspring.di.xml.Printer;
import myspring.di.xml.StringPrinter;
@Configuration
//<!-- Properties 파일 만들것이다. -->
//<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:config/values.properties"/>
@PropertySource("classpath:config/values.properties")
public class HelloConfig {
// Bean의 ID는 메서드이름이다.
@Value("${name}")
String name;
@Resource(name = "${printer}")
Printer printer;
@Bean
@Scope(value = "singleton")
public Hello hello(){
Hello hello= new Hello();
hello.setName(name);
//hello.setPrinter(stringPrinter());
hello.setPrinter(printer);
return hello;
}
@Bean
public Printer stringPrinter() {
Printer printer = new StringPrinter();
return printer;
}
@Bean
public Printer consolePrinter() {
Printer printer = new ConsolePrinter();
return printer;
}
}
이걸 이제 테스트쪽으로 가보면
@Autowired
Hello hello;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("hello")
Hello hello2;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("stringPrinter")
Printer printer;
@Test
public void consoleConfig() {
System.out.println(hello.sayHello());
hello.print();
}
@Test @Ignore
public void config(){
System.out.println(hello == hello2);
System.out.println(hello.sayHello());
hello.print();
System.out.println(printer.toString());
}
'Dev > [Java]' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Spring] 7. Mapper 써보기 (0) | 2021.02.01 |
|---|---|
| [Spring] 5. Database Connection Pool (DBCP)써보기, MyBatis Spring (0) | 2021.02.01 |
| [JAVA공부] 이클립스 단축키 정리 (0) | 2021.01.30 |
| [Spring] 2. Constructor Injection, DI전략2 어노테이션 써보기 (0) | 2021.01.29 |
| [Spring] 1. 라이브러리와 프레임워크의 차이점? DI전략1 (0) | 2021.01.29 |


